PREPARATION
With the Digital Transformation being one of the most discussed topics in the business world lately, many organizations find themselves struggling with the great paradigm shift and thus the implementation on the organizational, cultural and technological level. New technologies like the Internet of Things, Big Data, Advanced Analytics or Machine Learning are game changers for businesses. Appropriate understanding and use of new technologies will not only change the way in which customers perceive value but also influence how people work in the organization. It will also impact relationships with stakeholders. Regardless of these facts, the digital transformation does not end with the introduction of new technologies – cultural and organizational considerations are just as crucial.
The DIGITRANS project promises to support organizations with these strategic issues as it combines best practices with expert knowledge from diverse industries helping to create a better understanding of how to transform into the digital age.
What is a business model?
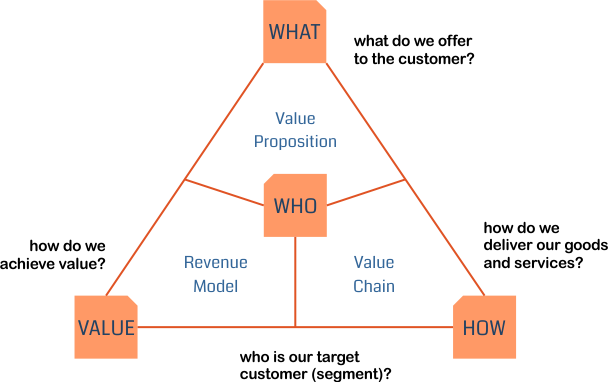
What makes a business model a digital one?
Business models, for which IT-Services play an important role for the value proposition of the product / service or even are the business service itself.
What are the main drivers for the digital transformation?
Increasing customer expectations: Everybody’s doing it.
There is a growing customer’s expectation of a digital experience due to the companies like Amazon, Netflix and Airbnb being recognized as digital service leaders. This forces non-digital companies to jump on the bandwagon to avoid becoming a “digital prey”.
Demand for speed and agility: Big vs. small becomes fast vs. slow.
The biggest obstacle arising from the digital transformation is the necessary change of the mindset. Businesses tend to think linear and the sudden demand to think “out of the box” is a great burden for the leaders. Enhancing digital competences and digital thinking on top management level is a crucial factor to success.
Know your customer: Customer insight is invaluable.
Gaining customer insight earlier by integrating them into the value creation can be invaluable. It does not only help in better matching the value proposition to the customers’ needs but it can also speed up the development of products and services and avoid moving in the wrong direction.
It’s not just digital: Digital transformation means business transformation.
Digital transformation involves partially reinventing the business overall, including its strategy, leadership ways, operations and culture. The main aim is to constantly increase the organization’s digital maturity on every level.
What are the pillars of the digital transformation?
The digital mindset: Thinking out of the box.
Adaptation of a new mindset is not only the biggest obstacle but also the most important success factor for the digital transformation. Leaders have to start “think digital” by being open-minded and embrace innovation in their company. Employees have to be encouraged to apply the digital mindset and participate in the transformation process.
The digital strategy: The company’s road map for the digital transformation.
In order to act properly and measure success, a business strategy is an imperative. On the way of the digital transformation, new obstacles will arise, the environment will change and adjustments will be required constantly along the way. Understanding these changes and knowing the path is utterly important to be successful in the digital age.
The skills: Learning to ride the wave.
Transformed environments with new technologies and cultures require new talents and profiles. Existing skills have to be adapted by continuous education of employees, complementing their original skills with digital competences and recruiting new ones with T-shaped profiles.
The technologies: Supporting the business with right technologies.
With all the new opportunities it brings, ignoring the latest technologies might put organizations at risk of falling behind the competition. However, carefully evaluating and selecting purposeful technologies – aligned to the digital strategy – is the key to success here. Technologies appear, change and also vanish so rapidly in the digital age, that backing the right horse is crucial for a sustainable technological foundation.
The evolution: Digital Transformation will not stop
It is inevitable to understand that the digital transformation is not going to stop and companies will find themselves on an everlasting journey with the need to adapt, rethink and reshape the company constantly.
What are current technological trends?
Internet of Things (IoT)

The Internet of Things describes the vision of the physical and digital worlds becoming one as a result of smart objects being connected through the Internet. Depending on the perspective, the focus can be put on the connected things themselves, the protocols or the opportunities and semantic challenges. The idea goes back to the early 90s with the vision of Ubiquitous Computing and has been developed further over the years with the term of Pervasive Computing as the precursor to the Internet of Things.
Simply put, IoT is the concept of connecting any device to the Internet (or a local network). It includes smart devices like phones or tablets as well as original dumb devices like lights, door locks or HVAC that are made smart by enhancing them with intelligence and network connectivity. The IoT trend is driven by decreasing costs of technologies and the sky-rocketing penetration of smart devices.
Blockchain
The blockchain technology describes an algorithm and distributed data structures for secure data transfers without a central administration (e.g. electronic cash transfers). It was originally designed for the crypto-currency Bitcoin and the blockchain concept was mainly driven by the rejection movement against money and bank-controlled payments regulated by governments. The original vision of the Bitcoin developers was to enable people to spend money without friction, intermediaries, regulations or the necessity to know or trust third parties.
Big Data

When searching the Internet for a definition of Big Data, one will inevitably stumble across the V-Model describing Big Data with its three dimensions: volume, velocity and variety. These dimensions make it difficult to handle with present technologies. Big Data is mostly unstructured data that exceeds the processing capacity of conventional database systems. It is too big, moves too fast or does not fit the structures of existing database architectures.
Machine Learning

The objective followed with Machine Learning is to enable machines to imitate and adapt human-like behaviour. This is done by teaching machines to learn from experience. Machine Learning algorithms contain methods to learn from data without relying on predetermined equations and thus memorizing it. The aim is to find natural patterns and get insights from data and ideally make predictions for data-driven decision making.
Examples for the use of Machine Learning are personal assistants like Siri, medical diagnosis or personalized shopping suggestions and ads.